
Gidon Almogy
Head of Surgery B, Hadassah University Hospital, Ein Kerem, Jerusalem
1986-1992 – Graduated Cum Laude from Hebrew University-Hadassah Medical School in Jerusalem
1994-2000 – Resident in General Surgery at the Department of General Surgery, Hadassah University Hospital, Ein Kerem, Jerusalem
1998-1999 – Fellowship in General and Laparoscopic surgery at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York
2002-2004 – Fellowship in open and laparoscopic surgery of the Foregut at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles
2000 – Board Certified General Surgeon
Surgical Procedures
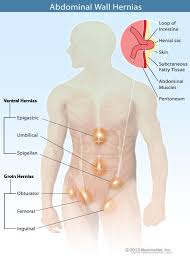
Hernia
Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder)
Splenectomy
Hernia
What: A hernia is a usually a defect in the abdominal wall such as an umbilical and supra-umbilical hernias, inguinal and femoral hernias, post-operative ventral hernias (incisional hernias), and diaphragmatic hernias.
Symptoms: Patients with abdominal wall and inguinal hernias may suffer from pain and swelling. The major complications of such hernias are an increase in size and incarceration of the hernia contents (usually bowel or fat) causing decreased blood flow, ischemia which may eventually lead to necrosis.
Surgery: Abdominal wall and inguinal hernias can be repaired using several techniques. Sutures are placed during primary repair. A synthetic mesh is often used to supplement or replace the suture repair. Different type of meshes are tailored for the different types of hernias. The repair can be performed either through an open approach or by the laparoscopic method. Each method has advantages and choosing the method should be tailored to the individual patient. Some of the techniques include open repair, laparoscopic repair with mesh, TEP and TAPP. Some of these methods can be performed under regional anesthesia.
Hospital Stay & Recovery: Length of stay following hernia repair ranges from an overnight stay to several days, depending on the technique of repair and complexity of the hernia.
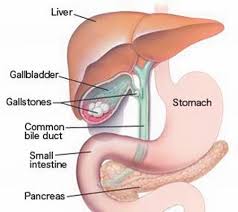
Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder removal)
Symptoms: Gallstones are formed due to several reasons. Patients suffering from gallstones will often complain of upper abdominal pain, more pronounced on the right-upper side of the abdomen, with worsening of symptoms after meals, usually meals with a high fat and or protein content.
Diagnosis: Gallstones are usually detected by abdominal ultrasound. Polyps of different sizes can also be found in the gallbladder.
Surgery: Cholecystectomy, or removal of the gallbladder, is usually performed using the laparoscopic approach (laparoscopic cholecystectomy). Several instruments including a camera are inserted into the abdominal cavity under general anesthesia.
Hospital Stay & Recovery: Length of stay following cholecystectomy ranges from an overnight stay to several days, depending on the complexity of the operation and on the patient’s overall condition.
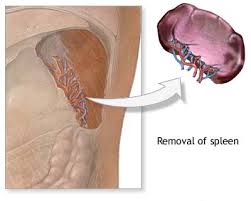
Splenectomy
What: The spleen is located in the left upper abdominal quadrant and has certain hematologic functions. In specific diseases the spleen needs to be removed (splenectomy).
Diagnosis: Patients are usually referred for splenectomy after hematologic consult.
Surgery: Surgery is performed under general anesthesia using the laparoscopic approach (laparoscopic splenectomy). Surgery is performed via several incisions and the spleen is usually removed through one of these incisions.
Hospital Stay & Recovery: Length of stay following laparoscopic splenectomy varies and ranges from 3-5 days depending on the complexity of surgery and the patient’s overall condition.
Following surgery the patient will require follow-up by family physician and hematologist, depending on the indication for splenectomy.
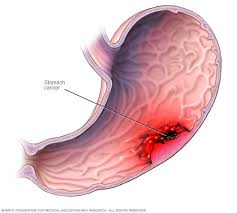
Gastric Tumors
Reflux
Gastric Tumors
What: Gastric tumors are composed of several types with varying malignancy rate. Common tumors in the stomach include adenocarcinoma, GIST, and gastric lymphoma.
Symptoms: Patients suffering from gastric tumors will often complain of epigastric abdominal pain, weight loss, early satiety, difficulty swallowing and weakness. Gastroscopy and gastric biopsy are usually diagnostic. The biopsy is sent for pathological evaluation.
Diagnose: Additional imaging studies will often include a CAT scan and/or PET scan. Some of the patients are sent for oncologic consultation pre-operatively. The goal of oncologic consultation is usually to help determine whether the patient should receive pre-operative (neo-adjuvant) chemotherapy.
Surgery: After all information is collected (gastroscopy, biopsy results, CAT scan report, etc.) the therapeutic approach is finalized. Partial or complete gastric resection (sub-total or total gastrectomy) are performed under general anesthesia. The resection can be performed by the open or laparoscopic approach (laparoscopic gastrectomy) depending on several factors. The resected stomach is sent for pathological evaluation to determine tumor staging and grading.
Hospital visit and recovery: Length of stay following gastrectomy ranges from one to two weeks, and depends on the complexity of surgery, tumor characteristics, and the patient’s overall condition. Following surgery, the patient gradually returns to a soft diet. Post-operative (adjuvant) treatment may include chemotherapy and radiation, depending on tumor characteristics.
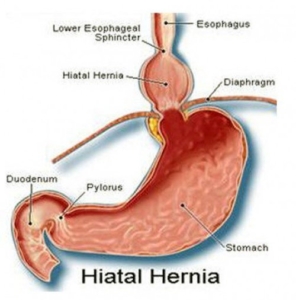
Diaphragmatic hernias and reflux disease
What: The stomach is characterized by an acidic environment. The lower esophageal sphincter functions as a physiological barrier between the acidic stomach and the neutral esophagus. In situations where the sphincter’s function is compromised, or when there is a diaphragmatic hernia, acidic fluid washes the esophageal mucosa (reflux) causing esophagitis and eventually may cause metaplasia.
Symptoms: Patients suffering from reflux will often complain of heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain and sometimes difficulty swallowing.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of reflux disease (GERD) is based several studies including gastroscopy, barium swallow, esophageal manometry and ph-metry of the esophagus.
Surgery: Some of the patients suffering from GERD will be referred for surgery. The goal of surgery is to ‘tighten’ the sphincter and repair the diaphragmatic hernia. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia using the laparoscopic approach. A laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is usually performed.
Hospital Stay & Recovery: Length of stay following laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair ranges from 3 to 5 days, and depends on the complexity of the hernia and the patient’s overall condition.
Make An Appointment
Get hafnia and hithayvut from your family physician.
Gather laboratory results, imaging studies such as ultrasound and CAT scan.
For public appointment call 02-5842111
For private appointment call 02-6778899
















